Cystoscopy Surgery in India
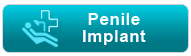
A method in which the specialist embeds a lit instrument called a cystoscope into the urethra (the tube that conveys pee from the bladder to the outside of the body) to peer inside the urethra and bladder.
The cystoscope has focal points like a telescope or magnifying instrument. These focal points let the specialist concentrate on the internal surfaces of the urinary tract. Some cystoscopes use optical strands (adaptable glass filaments) that convey a picture from the tip of the instrument to a review piece at the flip side. The cystoscope is as flimsy as a pencil and has a light at the tip. Numerous cystoscopes have additional tubes to manage different instruments for methodology to treat urinary issues.
Cystoscopy might be accomplished for any of various reasons including successive urinary tract diseases; blood in the pee (hematuria); loss of bladder control (incontinence) or an overactive bladder; irregular cells that have been found in pee test; the requirement for a bladder catheter; excruciating pee, interminable pelvic torment, or interstitial cystitis; urinary blockage, for example, prostate amplification, stricture, or narrowing of the urinary tract; an abnormal development, polyp, tumor, or malignancy: and a stone in the urinary tract.
Procedure
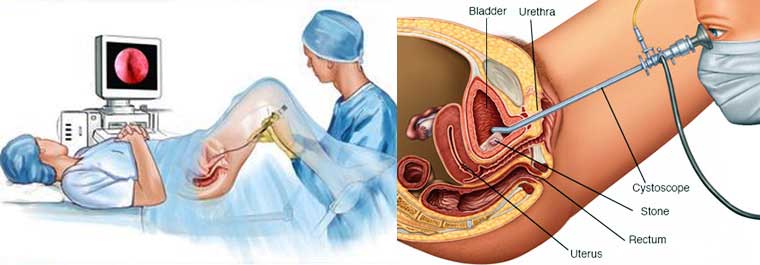
On the off chance that a stone is held up higher in the urinary tract, the specialist may broaden the cystoscope through the bladder and up into the ureter. (The ureter is the tube that conveys pee from the kidney to the bladder.) When used to see the ureters, the cystoscope is known as a ureteroscope. The specialist can then see the stone and evacuate it with a little wicker bin toward the end of a wire embedded through an additional tube in the ureteroscope. The specialist may likewise utilize the additional tube in the cystoscope to broaden an adaptable fiber that conveys a laser bar to break the stone into littler pieces that can then go out of the body in the pee. Ureteroscopy might be done under a spinal or general soporific.
For cystoscopy, the specialist delicately embeds the tip of the cystoscope into the urethra and gradually skims it up into the bladder. Unwinding the pelvic muscles makes this a player in the test less demanding. A clean fluid (water or saline) will move through the cystoscope to gradually fill the bladder and stretch it so that the specialist has a superior perspective of the bladder divider. As the bladder achieves limit, the patient feels some distress and the desire to urinate. (You will have the capacity to purge your bladder when the examination is over.) The time from insertion of the cystoscope to evacuation might be just a couple of minutes, or it might be longer if the specialist finds a stone and chooses to expel it. Taking a biopsy will likewise make the strategy last more. Much of the time, the whole examination, including arrangement, will take around 15 to 20 minutes.
Purpose
Cystoscopy is performed by urologists to inspect the whole bladder coating and take biopsies of any flawed regions. Cystoscopy might be endorsed for patients who show the accompanying conditions:
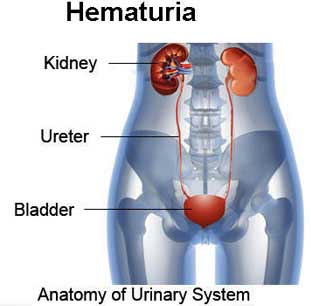
- Blood in the pee (Hematuria)
- Inability to control pee (incontinence)
- Urinary tract contamination
- Signs of innate variations from the norm in the urinary tract
- Suspected tumors in the bladder
- Bladder or kidney stones
- Signs or side effects of an amplified prostate
- Pain or trouble urinating (dysuria)
- Disorders of or wounds to the urinary tract
- Symptoms of interstitial cystitis
Blood and pee contemplates, notwithstanding x beams of the kidneys, ureters, and bladder, might be performed before a cystoscopy to acquire however much demonstrative data as could reasonably be expected. Amid the cystoscopy, a retrograde pyelogram may likewise be performed to analyze the kidneys and ureters.
After Care
After the test, there might be a gentle blazing feeling on pee and there may likewise be little measures of blood in the pee. These issues ought not last over 24 hours. Tell your specialist if draining or torment is serious or if issues last more than two or three days. To soothe uneasiness, drink two 8-ounce glasses of water every hour for 2 hours. You can scrub down to ease the smoldering feeling. If not, you might have the capacity to hold a warm, sodden washcloth over the urethral opening. You may give you an anti-infection to take for 1 or 2 days to keep a contamination. On the off chance that you have indications of contamination - including agony, chills, or fever - call your specialist. Patients who have experienced a cystoscopy are told to:
- Take steaming showers to mitigate torment.
- Rest and cease from driving for a few days, particularly if general anesthesia was utilized.
- Expect any blood in the pee to clear up in one to two days.
- Avoid strenuous activity amid recuperation.
- Postpone sexual relations until the urologist establishes that mending is finished.
Risks
As with any surgical strategy, there are a few dangers required with a cystoscopy. Confusions may incorporate abundant dying, a harmed urethra, a punctured bladder, a urinary tract disease, or a harmed penis.
Patients ought to contact their doctor on the off chance that they encounter any of the accompanying indications after the system, including torment, redness, swelling, waste, or seeping from the surgical site; indications of summed up disease, which may incorporate migraine, muscle throbs, discombobulation, or a general sick feeling and fever; sickness or heaving; or troublesome or agonizing pee.
Cystoscopy is an ordinarily performed methodology, however it is an intrusive procedure that includes little yet critical danger. In the event that anesthesia is required, there is extra hazard, especially for individuals who are large, smoke, or are in weakness. Those experiencing anesthesia must advise the specialist of any prescriptions they are taking.
Alternatives
There are systems that can give some data about the coating of the bladder, for instance, x beams; notwithstanding, none of these give as much data to the specialist as a cystoscopy.
Advantages of Cystoscopy Surgery in India
The little instrumentation connected to the cystoscope permits your specialist to evacuate little regions for biopsy, something that would not be conceivable with imaging considers. Little bladder stones may likewise be evacuated. Cystoscopy additionally allows urologists to convey exceptionally focused taking drugs to zones that are aroused or malignant.
| Copyright © 2024 www.edtreatmentindia.com All Rights Reserved. |